Table of Contents:
- What is WAN?
- The Importance of WAN in Business
- Types of WAN
- Advantages of Using WAN
- Challenges Associated with WAN
- WAN Security Best Practices
- Future of WAN Technology
- Conclusion
What is WAN?
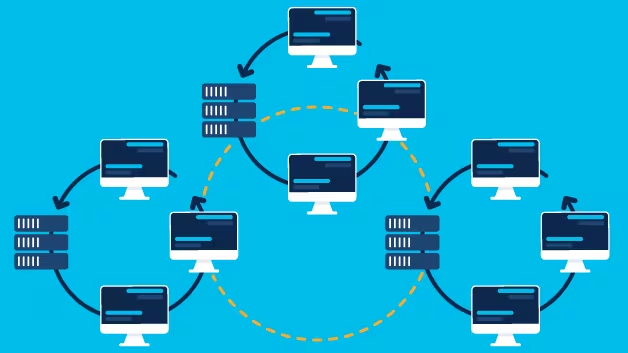
A WAN (Wide Area Network) is a telecommunications network designed to extend over large geographical areas. It’s primarily used for computer networking to manage resources and data exchange. Unlike local networks, WANs connect multiple smaller networks, including those separated by cities, regions, or even countries, making them significant players in today’s global connectivity. WAN technologies utilize various hardware and transmission media to achieve this expansive reach, ensuring that communication is maintained irrespective of distance.
In businesses, the application of WAN technology is indispensable. Companies can link branch offices across vast distances, facilitating seamless communication and effective resource management. WANs enable businesses to operate as a unified entity, ensuring that their IT infrastructure supports the workflows and requirements of all departments and locations. This is crucial for multinational corporations where synchronization of operations and data is vital for efficiency and profitability.
The Importance of WAN in Business
Modern businesses thrive on connectivity and real-time communication. WAN technology ensures that all local or international branch offices are connected efficiently. Integrating WAN into business operations enhances the sharing of critical data, supports collaboration, and maintains uniformity in business processes. It allows employees to access the same information, applications, and services, no matter their location, fostering a more collaborative and productive work environment.
For instance, some describe the essential nature of WAN technology for global businesses, underscoring the importance of reliable and secure wide-area networks. Companies that rely on WANs can operate more efficiently, as they can leverage centralized data centers, optimize bandwidth usage, and ensure quicker troubleshooting and maintenance operations, which are pertinent factors in today’s fast-paced business world.
Types of WAN
Point-to-Point WAN
This type establishes a direct connection between two locations, often suitable for secure and straightforward business communication. Point-to-Point WANs are characterized by their simplicity and reliability. They are ideal for organizations that require consistent and dedicated bandwidth between two sites. Such networks are commonly used for connecting main offices with remote data centers or large branches, ensuring that data can travel back and forth without interference or delay.
Packet-Switched WAN
Packet-switched WANs divide data into packets transmitted over shared networks, optimizing the usage of available bandwidth. This type of WAN can offer more flexibility and efficiency as it allows multiple data paths and supports dynamic bandwidth allocation. Technologies like MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) and Frame Relay are examples of packet-switched WANs, often used in environments where bandwidth optimization and cost efficiency are priorities.
Internet WAN
Internet WAN uses the public Internet to connect various networks. It’s cost-effective and widely used but requires robust security protocols. With an Internet WAN, businesses can leverage existing Internet infrastructure to establish wide-area connectivity. However, the reliance on public networks makes security paramount, necessitating VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) and other encryption methods to protect sensitive data during transmission.
Centralized WAN
This setup centralizes the WAN architecture to be managed from a single point, simplifying administration and improving control. Centralized WANs facilitate easier network management and configuration changes since they all stem from a central command. This model is particularly beneficial for organizations that streamline their network operations and reduce the complexity of managing multiple disjointed networks.
Advantages of Using WAN
Wide Area Networks offer various benefits that make them integral to modern business operations:
- Scalability: WANs are easily scalable, providing the capacity to connect new business locations as an organization grows. This scalability ensures that as a company expands its geographical footprint, its network infrastructure can scale up accordingly without requiring complete overhauls.
- Reliability: These networks deliver reliable communication solutions, ensuring all branches remain connected seamlessly. Downtime in communication can be detrimental for businesses, and WANs ensure high availability through redundant connections and robust architectures.
- Cost Efficiency: Businesses can significantly reduce travel costs and boost operational efficiency by connecting offices through WAN. The ability to conduct virtual meetings, share resources digitally, and operate centralized systems streamlines operations and reduces the need for physical travel, thereby saving logistics and travel expenses.
Challenges Associated with WAN
Despite its advantages, WAN technology comes with its own set of challenges:
- Latency: Given the extensive distances covered, latency can become a significant concern, affecting real-time communications. High latency can lead to delays in data transfer and negatively impact applications that require real-time interaction, such as video conferencing or VoIP communications.
- Security: Protecting data over large and dispersed networks can be complex and demands robust security measures. As data traverses multiple nodes and networks, it becomes susceptible to interception and attacks, making comprehensive security strategies indispensable.
- Cost: Businesses can find the initial setup and ongoing maintenance of WAN infrastructure expensive. Although WANs can bring long-term cost savings, the initial investment in equipment, technologies, and skilled personnel can be substantial, especially for smaller organizations.
WAN Security Best Practices
Businesses should implement robust security protocols within their WAN infrastructure to address security risks. Best practices include:
- Encrypted Connections: Encryption protects data during transmission. It ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties, thus preserving confidentiality.
- Firewalls: Implement advanced firewall solutions to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Firewalls are the first defense against potential threats and unauthorized access attempts.
- Regular Updates: Ensure all network software has the latest security patches and features. Regular updates help mitigate vulnerabilities and protect against newly discovered threats.
Future of WAN Technology
The evolution of WAN technology continues with innovations such as Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN). SD-WAN provide substantial improvements in flexibility, performance, and security. Its ability to intelligently manage traffic over multiple connections makes it increasingly popular among modern enterprises, paving the way for more dynamic, responsive network solutions. SD-WAN allow businesses to optimize traffic flow, enhance application performance, and reduce operational costs while maintaining high-security standards.
Moreover, advancements in technologies like 5G are set to complement WAN infrastructures, providing higher bandwidth and lower latency. As these technologies mature, businesses can expect their WAN solutions to become even more efficient and capable of supporting emerging applications and services, such as IoT (Internet of Things) and augmented reality (AR).
Conclusion
WAN technology is critical for the seamless operation of modern businesses. It offers a plethora of benefits while posing specific challenges. With ongoing advancements, particularly in SD-WAN, WAN technology is set to become even more integral to organizations’ success, ensuring they remain connected and competitive in the global market. Businesses leveraging WAN must stay abreast of these technological advancements and adopt best practices to mitigate challenges and maximize benefits.